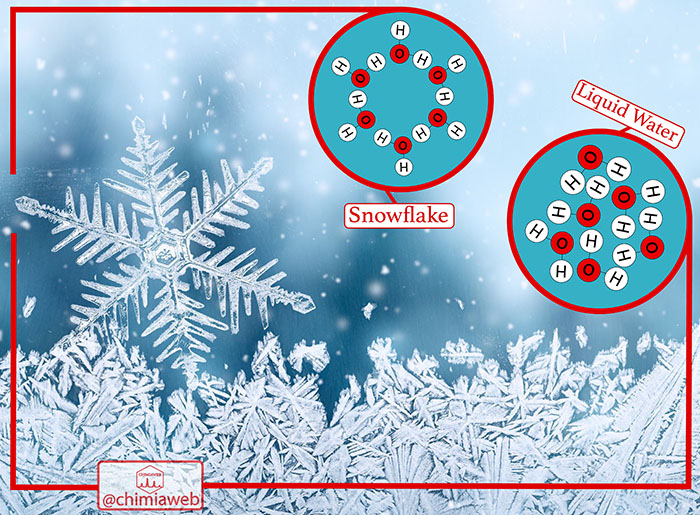
Snowflake is one of the nature’s wonders. It has a complex shape with various patterns. Actually, there are no two identical snowflakes in nature. These ice crystals are formed from frozen water molecules through a nucleation process.
Each water molecule is made up of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom. When the weather cools to a temperature below freezing, water molecules start to arrange themselves in a regular lattice. They chemically join together in a six-sided structure, called hexagonal.
The snow crystal shapes change extremely with temperature and humidity. Large plate-like crystals form when the weather is below freezing, while smaller plates and needles grow in colder degrees. In addition, high humidity levels give complex crystals, while simpler crystals develop in low humidity levels. A developing crystal experiences different weather conditions during its travel through the clouds. Since variations in the environmental condition can change the crystal formation, no two snowflakes are quite similar.
The next time you go out for snowflake watching, you will enjoy more observing the details of a snowflake when you know the science behind their dazzling shapes.