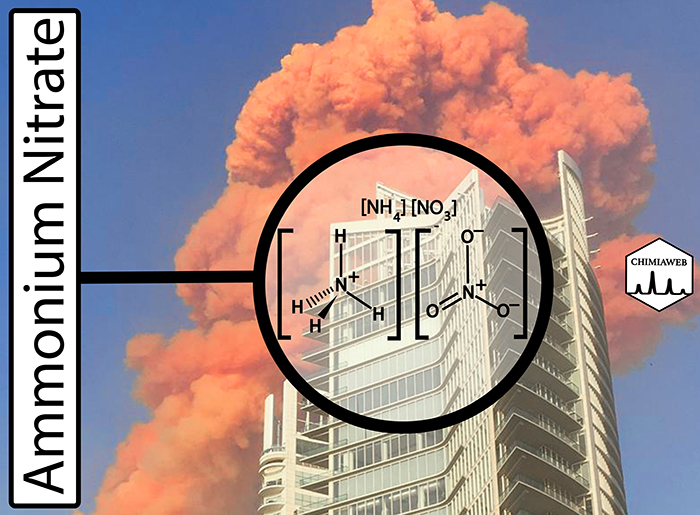
An ammonium nitrate explosion caused massive destruction in the port area of Lebanon’s capital, Beirut, on Tuesday (Aug. 4). This catastrophe is known to be one of the largest non-nuclear explosions in recent years.
Ammonium nitrate is a white crystalline solid, which is produced by the reaction of anhydrous ammonia with concentrated nitric acid. This chemical compound is widely used in fertilizer, as well as mining explosives.
Ammonium nitrate is relatively stable and harmless, but it undergoes decomposition explosively if heated under confinement or exposed to fire. When ammonium nitrate decomposes, it produces nitrogen gas (N2), oxygen gas (O2) and water vapor. Rapid volumetric expansion of gases causes the blast.
Toxic gases, including nitrogen oxides and ammonia, are also released in detonation. The reddish-brown gas that forms after blast is associated with nitrogen dioxide (NO2) gas, which is irritating to the respiratory system.