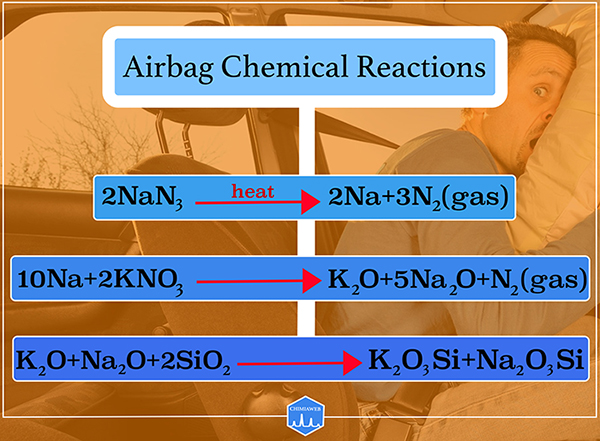
Airbag in automobile considerably decrease the chance of severe injuries during a crash. Here is a look at the mechanism through which airbags save lives. Actually, the airbag is filled with nitrogen (N2) gas generated by a rapid chemical reaction. Inside the airbag, there is a mixture of three compounds: sodium azide (NaN3), potassium nitrate (KNO3) and silicon dioxide (SiO2).
When a car collides something, a sensor is activated to generate heat. Sodium azide is decomposed by heat and produces sodium (Na) and nitrogen gas (N2). The generated nitrogen gas fills the airbag. Sodium should be removed, as its chemical reactivity is high. So the process is followed by the reaction of sodium with potassium nitrate (KNO3) to produce potassium oxide (K2O), sodium oxide (Na2O) and nitrogen gas. Eventually, metal oxides react with silicon dioxide (SiO2) to produce harmless potassium and sodium silicate (K2O3Si, Na2O3Si).